Over the past decade, India proved that open digital rails can break monopolies and create massive economic inclusion. But today, most future-defining innovation will not remain limited to code. It will shift into physical capability: manufacturing, robotics, material science, energy systems, medical biotech, agriculture biotech, and defense hardware.
The challenge is simple: unlike software, hardware innovation is expensive. CNC machines, furnaces, molds, prototyping tools, electronic benches, and testing infrastructure are locked behind capital barriers. This stops millions of capable Indians from becoming inventors.
Table of Contents
- Why India needs hardware + bio democratization
- Hardware public infrastructure: the missing layer
- Machine tool labs: the base of invention
- CNC & fabrication hubs for prototyping
- Furnaces, kilns & materials experimentation
- Molds, casting, tooling & repeatability
- 3D printing as fast iteration infrastructure
- Electronics labs: redesigning everyday products
- Bio labs: the next global battlefield
- Ancient Indian ingredients + modern product pipelines
- How government can build this sustainably
- Why this matters for 2030 world order
- Conclusion
1) Why India needs hardware + bio democratization
India has talent, ambition, and a growing startup ecosystem. But for most Indians, the cost of experimenting with hardware is extremely high. A single CNC machine can cost more than what many families earn in years.
That means hardware innovation gets concentrated in a few elite companies and top institutions. The result: ideas die before they become prototypes.
2) Hardware public infrastructure: the missing layer
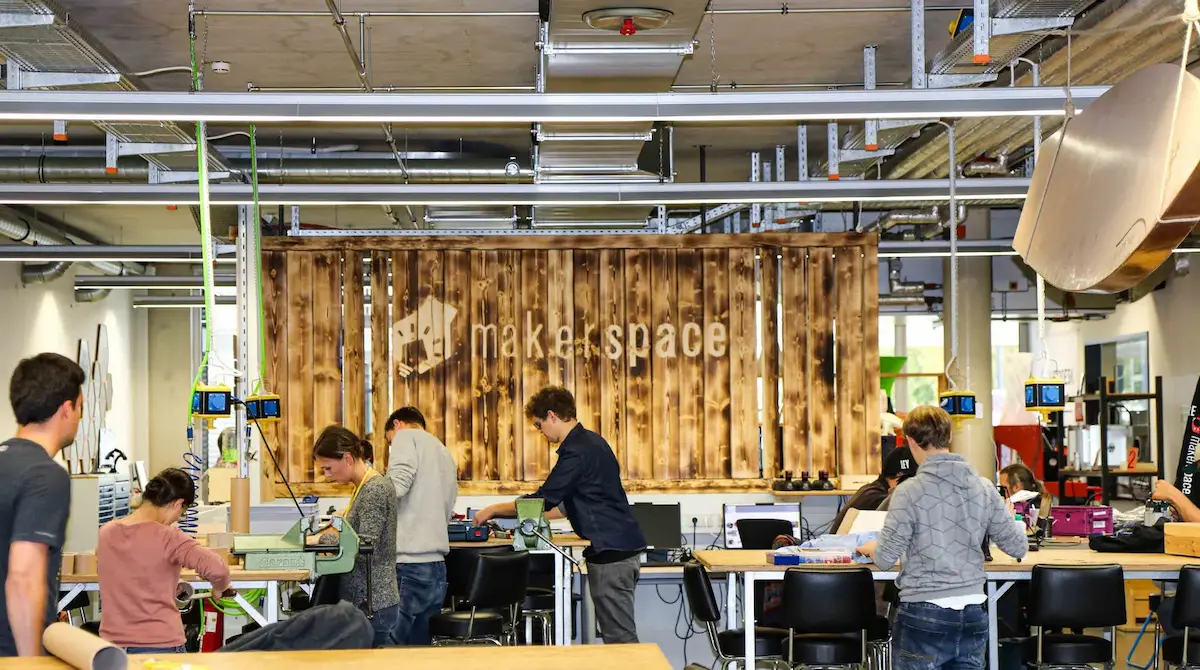

India created digital protocols that any company could build on top of. Now India needs physical infrastructure where any entrepreneur can build prototypes on top of:
- Machine tool labs (lathe, milling, grinding)
- CNC manufacturing access (pay-per-use)
- 3D printing + molds
- Furnaces + kilns + material labs
- Electronics benches + test equipment
Just like UPI removed barriers for payments innovation, hardware labs remove barriers for manufacturing innovation.
3) Machine tool labs: the base of invention
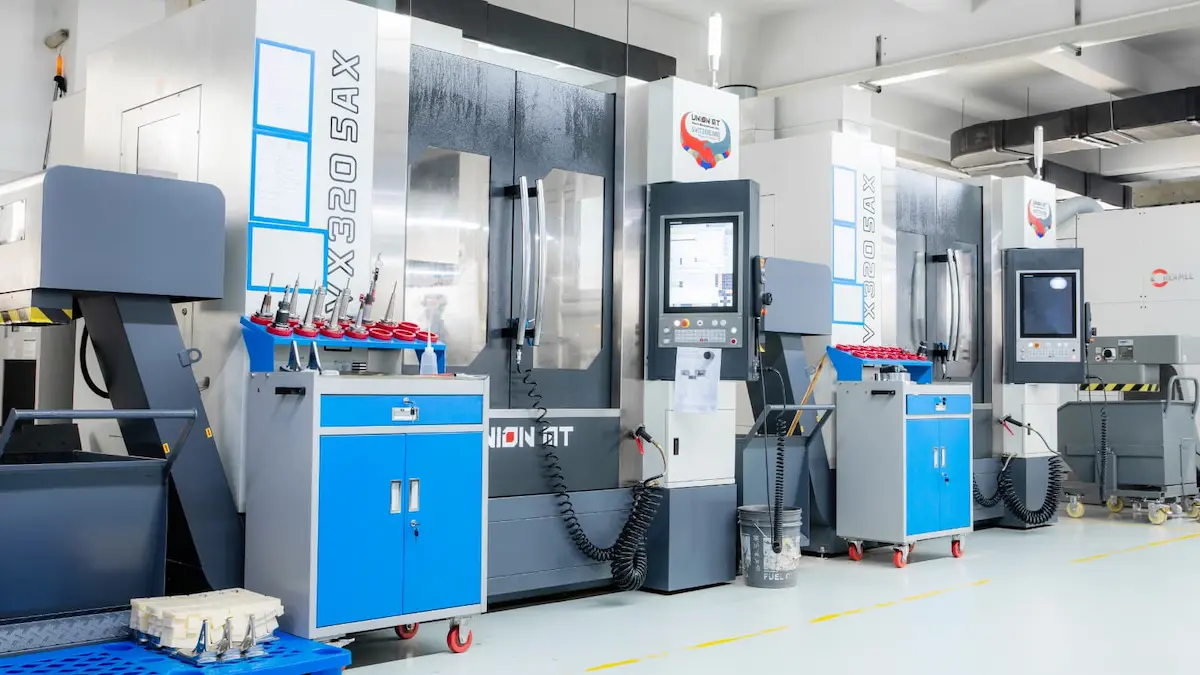

A machine tool lab is not glamorous like AI — but it is the foundation of real manufacturing strength. If India had public machine tool labs across districts and cities, then innovators could build prototypes of:
- Energy-efficient AC components
- More durable washing machine parts
- Agriculture tools for small farmers
- Repair + redesign parts for local manufacturing
4) CNC & fabrication hubs for prototyping
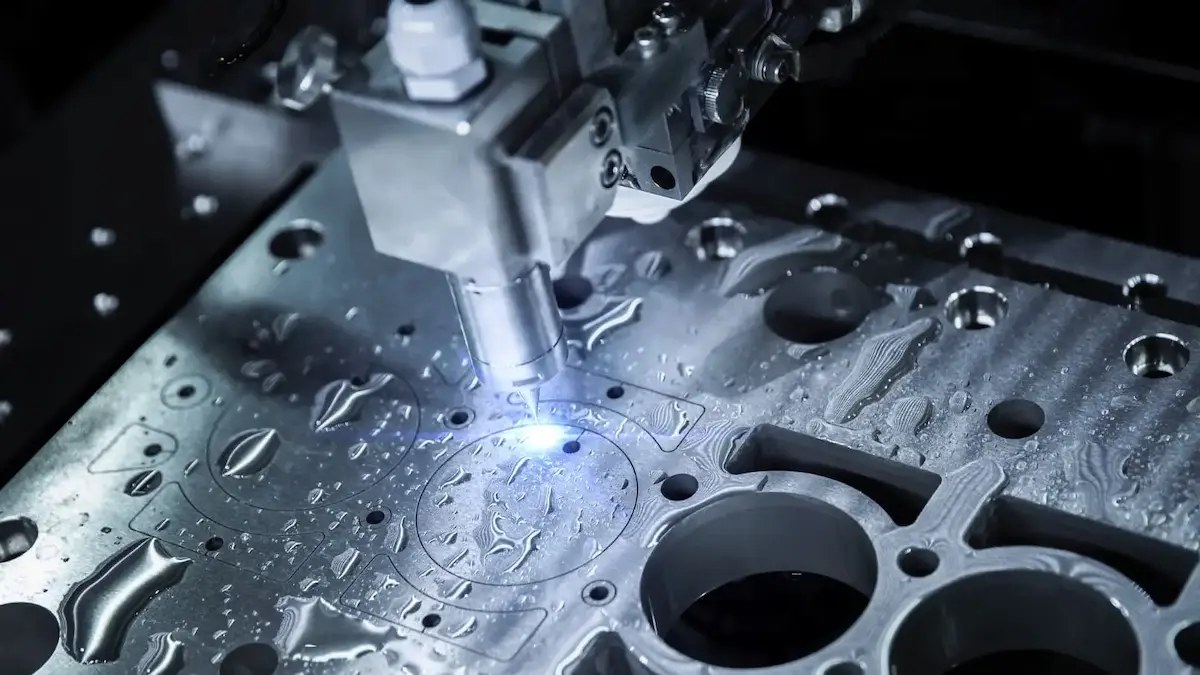

CNC labs allow makers to convert digital designs into high precision parts in hours. Without CNC access, even strong hardware ideas get stuck in “concept stage”.
A national CNC lab network can help India compete in industrial capability and defense manufacturing.
5) Furnaces, kilns & materials experimentation
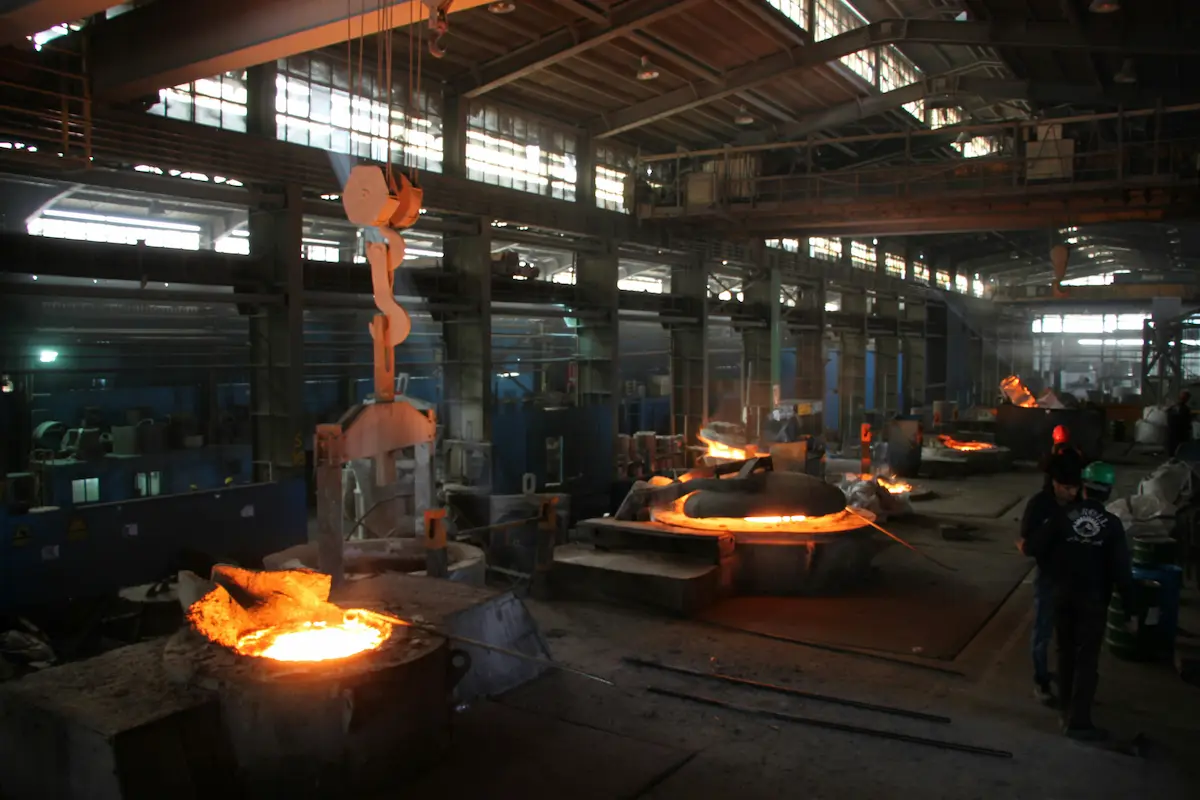

Many inventions require heat processing and controlled materials. Public furnaces and kilns allow experimentation in:
- Ceramics and composites
- Heat-treated metals
- Energy storage and insulation
- Industrial coatings
6) Molds, casting, tooling & repeatability

India must also democratize molds and tooling infrastructure because scaling hardware requires repeatability. Without tooling, hardware stays a prototype and never becomes a product.
7) 3D printing as fast iteration infrastructure
3D printing should be available like a public utility. It accelerates:
- Design testing
- Ergonomic improvements
- Prototype iteration
- Small batch market testing
8) Electronics labs: redesigning everyday products
India can build electronics innovation hubs where inventors can redesign or improve existing products:
- ACs (efficiency improvements)
- Washing machines (motor optimization)
- Low-cost automation tools for MSMEs
- Smart sensors for agriculture
9) Bio labs: the next global battlefield

Bio labs can democratize biotech innovation like hardware labs democratize manufacturing. India needs controlled public bio-lab infrastructure for:
- Food and fermentation research
- Health diagnostics innovation
- Agriculture biotech experimentation
- Natural ingredient formulation testing
10) Ancient Indian ingredients + modern product pipelines
India can build a unique biotech advantage by combining ancient Indian knowledge and ingredients with modern manufacturing and lab-based validation.
Entrepreneurs should be able to innovate across categories:
- Soaps & cosmetics with Indian botanical ingredients
- Ayurvedic food innovations
- Natural agriculture inputs
- Medicines and wellness formulations (with proper safety + testing)
11) How government can build this sustainably
These labs should be operated with:
- Pay-per-hour access model
- Training + certification for dangerous tools
- Strict safety SOPs for machines and bio-work
- Local partnerships with universities and MSMEs
12) Why this matters for 2030 world order
The next global competition will not be decided only by apps. It will be decided by manufacturing capability, bio capability, supply chains, defense readiness, and the ability to rapidly innovate in hardware.
India can become a true innovation nation if it makes invention accessible for the mass population — not only for a privileged few.
Recommended tools & resources
If you want to learn hardware innovation and public infrastructure thinking, these resources can help.
Disclosure: Links may be affiliate links. See Disclaimer.
Conclusion
India showed the world how democratized digital infrastructure can unlock scale. The next transformation must be physical.
By democratizing machine tool labs and bio labs as public infrastructure, India can unlock an era where inventors, entrepreneurs, and creators can build world-class products with low initial capital — and strengthen national capability for the decade ahead.